Traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) are the most severe injuries a person can experience. It may be due to several reasons, such as a vehicle accident, sports accident, or a fall from a height because of someone else’s negligence.
A TBI can lead to severe physical, emotional, and cognitive challenges as it directly affects the brain.
The consequences of TBI can be life-altering and long-lasting. Some injuries may seem minor but slowly develop and affect the brain later.
You should know some of the life-altering impacts of TBIs so that you can get proper medical treatment on time and file a lawsuit to claim compensation for your losses with the help of traumatic brain injury lawyers.
What is a Traumatic Brain Injury?
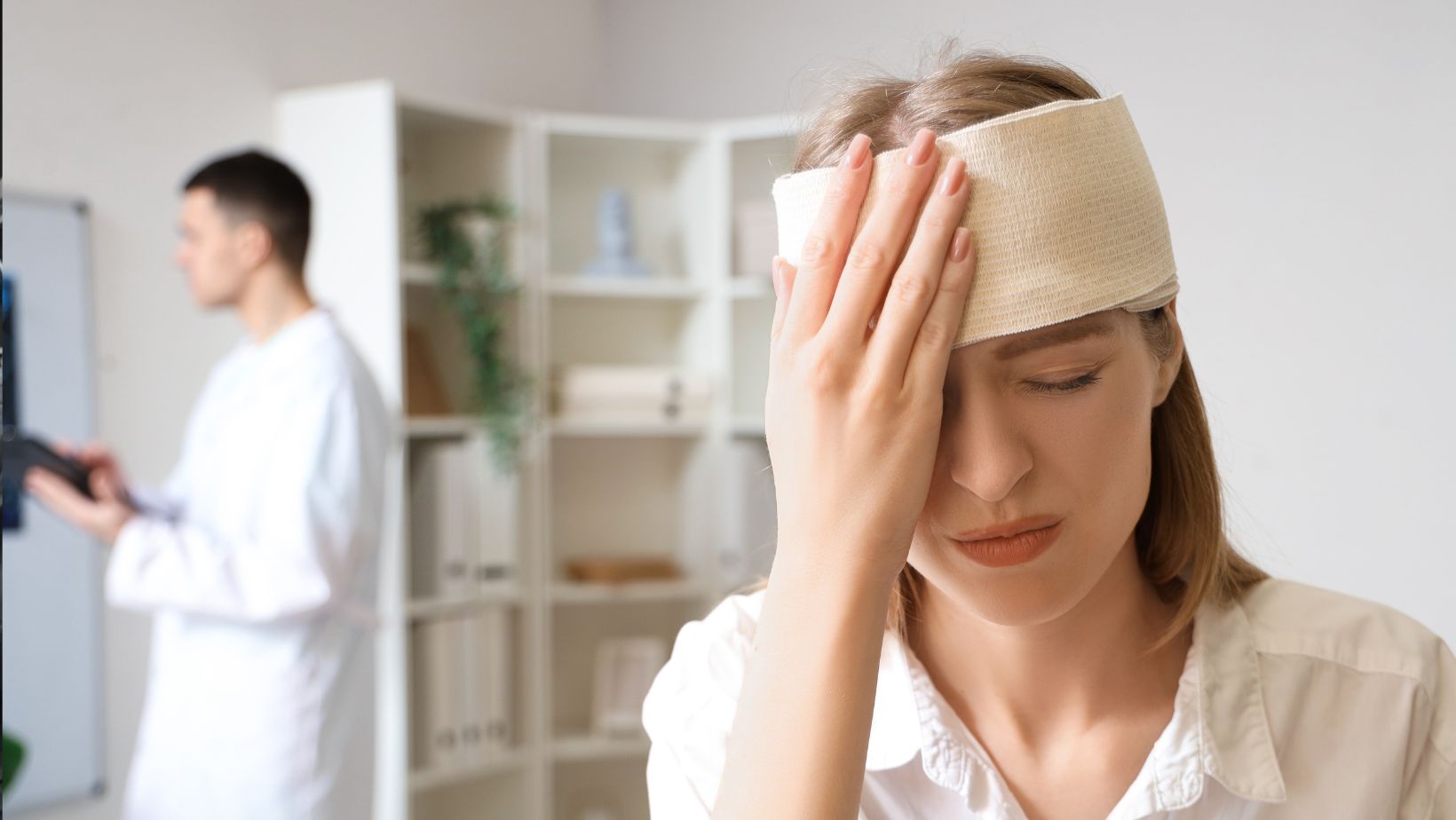
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is an acquired brain injury that may occur when an external force causes damage to the brain. It can happen when the head suddenly hits an object in a situation like a vehicle accident or when an object pierces the skull and enters the brain tissue. This greatly affects brain function. The impacts of TBI can be very severe. Here are some of the life-altering effects of TBI.
Physical Impairments and Loss of Independence
TBI can lead to severe physical impairments, which can alter daily life. When the brain gets injured, people may struggle to walk due to weakness in certain limbs. Sometimes, limbs get paralyzed.
Loss of coordination or fine motor skills can make everyday activities like dressing, eating, or driving difficult. In more severe cases, individuals require around-the-clock care for the rest of their lives. This loss of independence can be stressful and affect a person’s self-esteem.
Cognitive and Memory Impairments
Another major effect of TBIs is their impact on cognitive functions. The brain plays a central role in all aspects of our daily lives, such as memory, decision-making, and problem-solving. If an individual is affected by a TBI, they may have issues with memory retention, concentration, and mental clarity.
They may also forget things and have difficulty recalling past experiences. These cognitive impairments affect professional and personal life. For some, these memory issues can continue for months or even years after the injury, severely limiting their ability to work, do household chores, or even pursue hobbies.
Emotional and Behavioral Changes
TBIs not only affect cognitive abilities but also change a person’s emotional response and behaviors. People experience mood swings, irritability, depression, or even aggressive behaviors. This will affect personal relationships, as the person with a TBI may seem easily frustrated or less patient than before.
Even family members, friends, and partners may find it hard to handle them, which may create an emotional distance between them. So, TBIs can affect both the person and the members around them.
Long-Term Health Effects
While some individuals may recover partially or fully from TBI, for some people, it can last a lifetime. Over time, individuals who have experienced a TBI may be at an increased risk for developing other health problems, including chronic headaches, sleep disturbances, seizures, and vertigo.
Additionally, they are more susceptible to neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease or chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE). This can gradually decline the quality of life and increase the long-term effects.
Coping and Treatment
Even though recovering from TBI is not easy, there are some treatment options available to help manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life. Here are the common treatment options:
- Physical Therapy: It helps regain motor skills and improve coordination.
- Cognitive Therapy: It can address memory, attention, and other mental issues.
- Speech Therapy: This helps individuals with difficulties speaking, swallowing, or understanding language.
- Psychotherapy and Counseling: It can help manage emotional and behavioral changes, including depression and anxiety.
- Medications: This will address symptoms such as pain, depression, or irritability.