Key Takeaways:
- Joint replacement surgery is a highly effective option for those suffering from chronic joint pain, offering a path to pain-free movement and an improved quality of life.
- The procedure involves replacing damaged or diseased joints with artificial implants, most commonly performed on the hip, knee, shoulder, elbow, ankle, and wrist.
- Conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, post-traumatic arthritis, avascular necrosis, congenital joint disorders, and severe injuries often lead to the necessity for joint replacement surgery.
Does the thought of climbing the stairs leave you winded, or has that daily walk become a battle against your own body? Chronic joint pain can significantly impact your life, limiting your mobility and independence. But what if there was a solution? Joint replacement surgery offers a powerful option for regaining pain-free movement and reclaiming your active life.
That said, this guide dives deeper than just the promise of pain relief. It will explore what it is, how the surgery works, and the reasons why someone might choose to undergo this procedure. So, keep reading to see if joint replacement could be the key to getting you back on your feet.
What Is Joint Replacement?
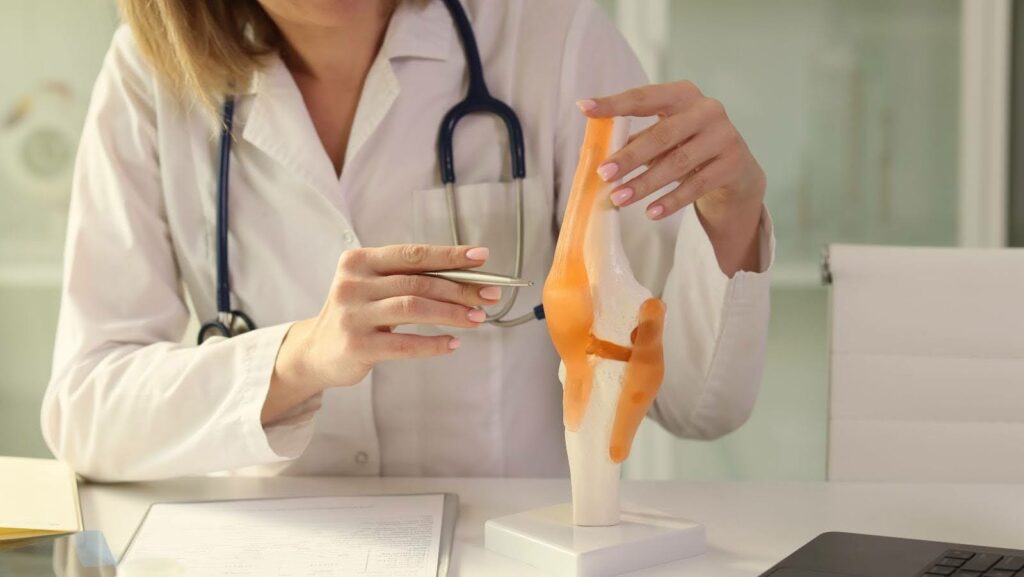
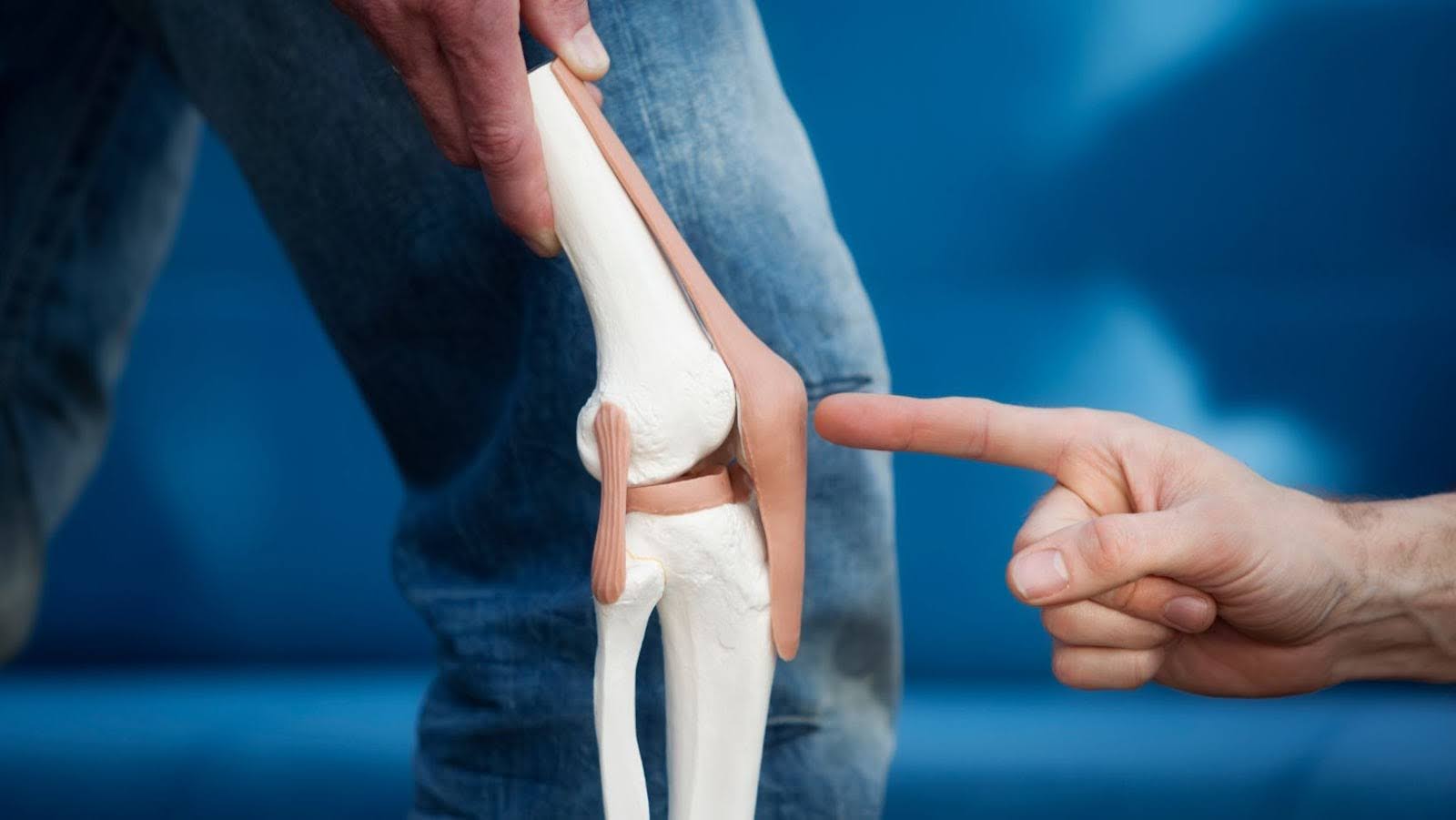
Joint replacement or arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which a damaged or diseased joint is removed and replaced with an artificial implant, known as a prosthesis. This surgery is mostly performed by an orthopedic surgeon on weight-bearing joints such as the hip and knee, but it can also be done on the shoulder, elbow, ankle, and wrist.
Purpose Of Joint Replacement
The main reason people opt for joint replacement surgery is to bid farewell to pain, get their joint working like a well-oiled machine again, and enjoy a better quality of life. This is especially true for those dealing with severe joint issues that make everyday activities a struggle. These problems often stem from chronic conditions like osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis, injuries, or other wear-and-tear disorders that cause the joint to break down and stop functioning properly.
Common Types Of Joint Replacements
Joint replacement surgery is a widely performed procedure aimed at replacing damaged or diseased joints with artificial implants to restore function and alleviate pain. Here are the most common types of joint replacements:
Hip Replacement
If you’re dealing with a worn-out hip joint that’s causing you pain and limiting your mobility, your doctor might suggest hip replacement surgery, also called hip arthroplasty. During this procedure, the surgeon will swap out your damaged hip joint with a shiny new prosthesis made of metal, ceramic, or plastic parts. This surgery is usually recommended for folks with severe hip arthritis, hip fractures, or conditions like avascular necrosis. When it comes to hip replacement, there are two main options to choose from:
- Total Hip Replacement (THR): Both the femoral head (the ball) and the acetabulum (the socket) are replaced.
- Partial Hip Replacement (Hemiarthroplasty): Only the femoral head is replaced.
Knee Replacement
Knee replacement surgery, or knee arthroplasty, is performed to replace the damaged surfaces of the knee joint with metal and plastic components. It is primarily done for patients with severe knee arthritis, including osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Types of knee replacement include:
- Total Knee Replacement (TKR): The entire knee joint is replaced, including the femur, tibia, and patella.
- Partial Knee Replacement (PKR): Only the affected compartment of the knee (medial, lateral, or patellofemoral) is replaced.
Shoulder Replacement
If your shoulder joint is giving you grief and nothing seems to help, your doctor might suggest shoulder replacement surgery, also known as shoulder arthroplasty. During this procedure, the surgeon will swap out the damaged bits of your shoulder joint with a shiny new metal ball and a plastic socket. This surgery is often the go-to solution for folks dealing with severe shoulder arthritis, rotator cuff injuries, or fractures that just won’t heal. When it comes to shoulder replacement, you’ve got a few options to choose from:
- Total Shoulder Replacement: Both the humeral head (ball) and the glenoid (socket) are replaced.
- Reverse Shoulder Replacement: The positions of the ball and socket are switched, which is beneficial for patients with rotator cuff arthropathy.
Elbow Replacement
If your elbow is really damaged from arthritis or an injury, your doctor might suggest swapping it out for artificial metal and plastic parts. This surgery, called an elbow replacement, is usually done for folks with rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, or elbow fractures. Here are two ways they do this operation:
- Total Elbow Replacement: Both the humerus (upper arm bone) and the ulna (forearm bone) are replaced.
- Partial Elbow Replacement: Only one part of the elbow joint is replaced.
Ankle Replacement
Ankle replacement surgery, or ankle arthroplasty, involves replacing the damaged ankle joint with a prosthesis made of metal and plastic. This surgery is less common than hip or knee replacements but is performed for patients with severe ankle arthritis or injury. The procedure aims to relieve pain and maintain ankle movement.
Wrist Replacement
Wrist replacement surgery, or wrist arthroplasty, is performed to replace the damaged wrist joint with metal and plastic components. This procedure is recommended for patients with severe wrist arthritis, particularly rheumatoid arthritis. The goal is to relieve pain and improve wrist function.
Each type of joint replacement is tailored to address specific conditions and needs, helping patients regain mobility and enhance their quality of life.
Medical Conditions Leading To Joint Replacement
Joint replacement surgery is often recommended for individuals suffering from severe joint damage and chronic pain that do not respond to conservative treatments. Several medical conditions can lead to the necessity for joint replacement. Here are the primary conditions:
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the most common reason for joint replacement surgery. This degenerative joint disease results from the gradual breakdown of cartilage, the cushioning material at the ends of bones. As cartilage wears away, bones begin to rub against each other, causing pain, swelling, and reduced joint mobility. Osteoarthritis primarily affects weight-bearing joints such as the hips and knees, but it can also impact the shoulders, hands, and spine.
Over time, the pain and stiffness associated with osteoarthritis can become debilitating, severely impacting a person’s ability to perform daily activities. When conservative treatments such as medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications fail to provide relief, joint replacement surgery becomes a viable option to restore function and alleviate pain.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
If you have rheumatoid arthritis, your body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the lining of your joints, causing painful swelling and stiffness. Over time, this constant inflammation can seriously damage your joints, leading to deformities and loss of movement. Rheumatoid arthritis is different from osteoarthritis, which mainly affects the cartilage.
Smaller joints in the hands and wrists are often impacted by rheumatoid arthritis, but it can also strike larger joints like knees and shoulders. When the damage becomes severe, joint replacement surgery can be a life-changing solution, easing pain, restoring function, and stopping the progression of joint destruction.
Post-Traumatic Arthritis
Post-traumatic arthritis develops after an injury to a joint, such as a fracture, dislocation, or ligament tear. These injuries can damage the cartilage and alter the mechanics of the joint, leading to arthritis over time. Unlike osteoarthritis, which develops gradually with age, post-traumatic arthritis can occur relatively quickly after an injury.
This condition can affect any joint but is most common in the hips, knees, and ankles. Symptoms include joint pain, swelling, and stiffness, which can worsen over time. When conservative treatments do not alleviate the symptoms, joint replacement surgery may be necessary to restore joint function and improve mobility.
Avascular Necrosis
Avascular necrosis (AVN) happens when the blood supply to a bone gets cut off, causing that bone tissue to basically die. This can make the joint surface collapse and lead to bad arthritis. AVN often strikes the hip but can also mess up the shoulders, knees, and ankles.
Causes include injuries, long-term use of heavy steroid doses, drinking too much alcohol, and certain medical conditions like sickle cell disease. The pain from AVN can be intense and crippling, often requiring surgery to replace the joint and get rid of the pain and get the joint working again.
Congenital Joint Disorders
Congenital joint disorders include conditions present at birth that can lead to joint problems later in life. Examples include hip dysplasia, where the hip socket does not fully cover the ball portion of the upper thighbone, and congenital knee dislocation. These disorders can cause joint instability, abnormal movement, and early-onset arthritis.
Individuals with congenital joint disorders may experience significant pain and functional limitations as they age. Joint replacement surgery can provide a solution by correcting the deformity, relieving pain, and improving joint function, thereby enhancing the patient’s quality of life.
Other Inflammatory Joint Diseases
Inflammatory joint diseases like lupus and gout can also mess up your joints and make you need a replacement. Lupus is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation all over, including in the joints, leading to pain and damage. Gout is a type of arthritis caused by uric acid crystals building up in the joints, causing crazy pain and inflammation.
If these conditions aren’t managed well, they can cause long-term joint damage. When diseases like these really deteriorate your joints, surgery to replace the joint may be needed to help you move again and get rid of the pain.
Severe Joint Injuries
Joint injuries from accidents or nasty falls can really mess up the cartilage, ligaments, and bones that make up the joint. Over time, this damage can cause arthritis and may require a joint replacement. Things like fractures, dislocations, and torn ligaments can throw off how the joint moves, leading to chronic pain and instability. When treatments like physical therapy or braces don’t get the joint working right again, surgery to replace the joint can help get rid of the pain and improve mobility.
Tumors
Bone tumors, whether benign or malignant, can affect the structure and function of joints. Surgical removal of tumors sometimes requires joint replacement to restore function and relieve pain. Benign tumors can weaken the bone, leading to fractures and joint instability. Malignant tumors, such as osteosarcoma, can destroy bone tissue and necessitate the removal of a significant portion of the bone. In such cases, joint replacement surgery can help rebuild the joint, allowing patients to regain function and improve their quality of life.
Joint replacement surgery provides a solution for individuals with these conditions when other treatments have failed to alleviate pain and restore function.
The Joint Replacement Procedure
Joint replacement surgery is a well-established medical procedure designed to replace damaged or diseased joints with artificial implants, aiming to restore function and alleviate pain. The process involves several stages, including the following:
Preoperative Preparation
Preoperative preparation is crucial to the success of joint replacement surgery. This phase includes several steps to ensure the patient is ready for the procedure:
- Medical Evaluations: The patient undergoes comprehensive medical evaluations, including blood tests, imaging studies (X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans), and physical examinations. These assessments help determine the extent of joint damage and identify any underlying health conditions that might affect surgery.
- Pre-Surgery Education and Planning: Patients attend preoperative education classes or counseling sessions to understand the surgery, the recovery process, and the potential risks and benefits. This preparation helps alleviate anxiety and ensures patients know what to expect.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Patients may need to make lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, quitting smoking, or improving their overall fitness, to enhance surgical outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
Surgical Techniques
The surgical techniques used in joint replacement vary depending on the type of joint being replaced and the patient’s specific needs. Here are the primary surgical approaches:
- Traditional Open Surgery: With this traditional approach, the surgeon makes a bigger cut to get to the joint. They remove the messed up joint surfaces and replace them with artificial parts. While it works, this method usually means a longer recovery since the cut is bigger and there’s more disruption to the surrounding tissues.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery: Minimally invasive techniques involve smaller incisions and less tissue damage. This approach can lead to shorter hospital stays, reduced pain, and faster recovery times. However, not all patients are candidates for minimally invasive surgery, depending on the severity and complexity of their joint condition.
Types of Implants and Materials Used
The success of joint replacement surgery depends significantly on the type of implants and materials used. These prosthetic components are designed to mimic the natural movement and function of a healthy joint. Common materials include:
- Metal Implants: Metals such as stainless steel, cobalt-chromium alloys, and titanium are commonly used in joint replacements. They are durable and provide excellent support and stability.
- Ceramic Implants: Ceramic components are used in some joint replacements due to their smooth surface and wear resistance. They are often used in hip replacements to reduce the risk of metal-on-metal contact and wear.
- Polyethylene Implants: High-density polyethylene is a plastic material commonly used for the bearing surfaces of joint replacements. It provides a smooth, low-friction surface that reduces wear and tear on the joint.
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation
Successful recovery from joint replacement surgery depends on effective postoperative care and rehabilitation. This phase includes several key components:
- Immediate Post-Surgery Care: After surgery, patients are monitored closely in the hospital for any complications. Pain management is a critical aspect of immediate postoperative care, involving medications to control pain and reduce inflammation.
- Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy: Physical therapy begins soon after surgery, often within a day or two. The primary goal of rehabilitation is to restore joint function, improve mobility, and strengthen the surrounding muscles. A typical rehabilitation program includes exercises to enhance range of motion, strength training, and functional activities.
- Long-Term Recovery and Lifestyle Adjustments: Long-term recovery involves gradually returning to daily activities while avoiding excessive strain on the new joint. Patients are advised to follow their surgeon’s recommendations regarding activity levels and precautions to prevent complications. Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor the implant’s condition and ensure optimal joint function.
Conclusion
Joint replacement surgery can be a life-changing procedure, offering a path back to pain-free mobility and an active life. However, it’s important to remember that this decision requires careful consideration. This guide has equipped you with the knowledge to navigate this process. Now, you can discuss your options with a healthcare professional to determine if joint replacement is the right choice for you.